What Are the Key Components of Industrial Ball Valves and Their Functions?
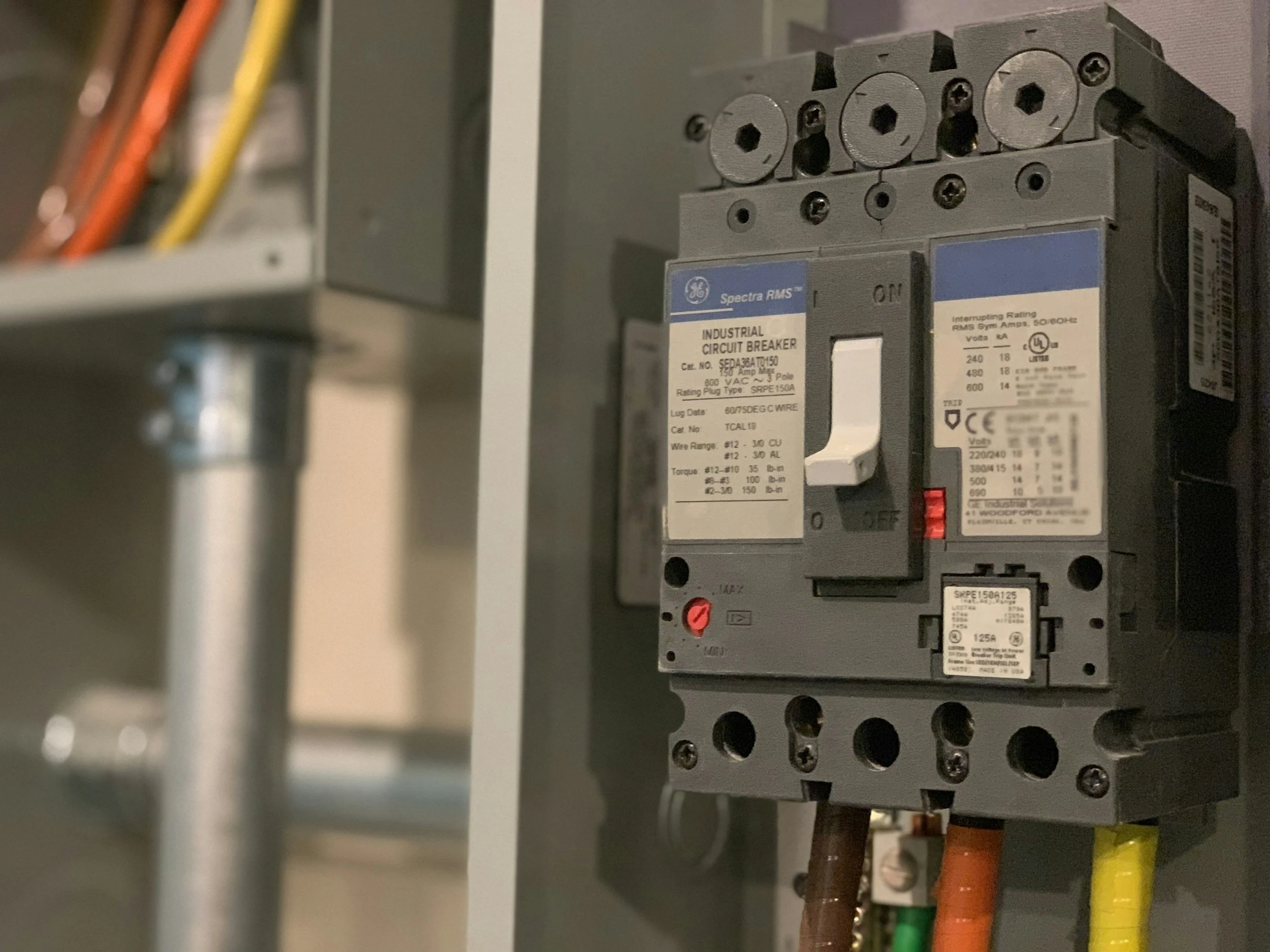
Industrial ball valves are integral in many piping systems, ensuring efficient and reliable flow control. Key components of industrial ball valves include the valve body, ball, seats, stem, and actuator, each playing a vital role in the valve's functionality. Understanding these parts is crucial for selecting the right valve for various applications, such as in oil and gas, chemical processing, and HVAC systems.
The valve body houses all internal components and provides the main pressure boundary. The ball, often made from durable materials like stainless steel, rotates to control the fluid flow. The seats support and seal the ball, while the stem connects the ball to the actuator, which is responsible for the movement of the ball.
For those maintaining or replacing parts, it's important to consider the availability of durable ball valve parts; high-quality materials and precise engineering ensure longevity and performance in demanding environments.
Key Takeaways
Industrial ball valves consist of several crucial components including the valve body, ball, seats, and stem.
Each part plays a specific role essential to the valve's overall functionality and efficiency.
Durable materials and reliable parts ensure long-term performance in various industrial applications.
Understanding Ball Valves
Ball valves are essential components in fluid control systems, designed for efficient regulation by controlling flow through a rotating ball. Understanding the key components and materials used in ball valves can enhance performance and durability in various industrial applications.
Overview of Ball Valve Components
Ball valves consist of several critical components that work together to control fluid flow. The ball itself is a spherical part with a hole or port that aligns with the flow path when in the open position, allowing fluid to pass. The stem connects the ball to the external control mechanism, such as a handle or actuator, enabling rotation.
The body of the valve houses these components and provides the structure. Seats are ring-shaped seals that ensure a tight closure, preventing leaks when the valve is off. The sealing mechanism is crucial for maintaining fluid isolation and system integrity under varying pressure and temperature conditions. Packing around the stem further prevents leakage.
An actuator or handle is used to manually or automatically control the valve's position, making it either open or closed.
Material Selection for Durability and Performance
The materials used in ball valves are vital for ensuring long-term performance, durability, and resistance to environmental factors. Brass, stainless steel, and PVC are commonly used materials.
Brass is often selected for its excellent machinability and decent corrosion resistance, suitable for many industrial and plumbing applications. Stainless steel offers superior corrosion resistance and strength, ideal for high-temperature and high-pressure conditions. PVC is a lightweight, corrosion-resistant option often used in lower pressure and temperature systems.
Choosing the right material depends on the specific requirements of the application, including temperature, pressure, and the type of fluid being controlled. Each material provides different advantages, balancing factors like cost, strength, and corrosion resistance.
Functional Dynamics of Ball Valves
Ball valves function by controlling the flow of a fluid or gas through a pipe using a spherical disc. These valves are distinguished by their reliability and ease of operation, making them a key component in many industrial applications.
Mechanics of Opening and Closing
A ball valve opens and closes through a quarter-turn rotation of a spherical ball. The ball, containing a bore through its center, allows fluid to pass when the bore is aligned with the pipeline. Rotating the ball 90 degrees blocks the flow.
This simple mechanism is operated via various actuators such as manual levers, electric motors, pneumatic systems, or hydraulic actuators. Manual levers are common for small valve sizes, while electric or pneumatic actuators are frequently used for larger or automated systems. The rapid, quarter-turn operation minimizes wear and tear, contributing to a long service life and high reliability.
Operational Considerations
Several factors influence the operational efficiency of ball valves. Temperature and pressure ratings are critical, as these valves must withstand varying conditions without compromising the flow control. High-quality seats create tight seals to prevent leaks, ensuring safety.
Valve size and bore dimensions impact fluid dynamics. Larger bores facilitate better flow with minimal pressure drop, while smaller valves may be better for precise control. Material selection for the ball and seats is crucial for handling different fluids and temperatures.
In industrial settings, ball valves are preferred for their durability and the ability to maintain consistent pressure and flow control, which is essential for process safety and reliability. Their flexibility in applications and actuator compatibility makes them suitable for various operational needs.
Conclusion
Ball valves are indispensable components in industrial applications due to their efficiency and reliability. The core elements, including the spherical ball, stem, and seats, collaborate to provide precise control over fluid flow.
Their durability and ease of operation make them a preferred choice in various industries. Selecting the right type and understanding each part's function enhances operational efficiency and safety.